Background: Surgical resection of WHO grade 2 meningioma can be curative. [68Ga]-DOTATATE PET imaging is more sensitive than gadolinium-enhanced MRI for detection of residual meningioma following surgery. We explored the progression-free survival prospects of patients who had undergone an radiographically complete resection of a WHO grade 2 meningioma as assessed by both MRI and [68Ga]-DOTATATE PET.
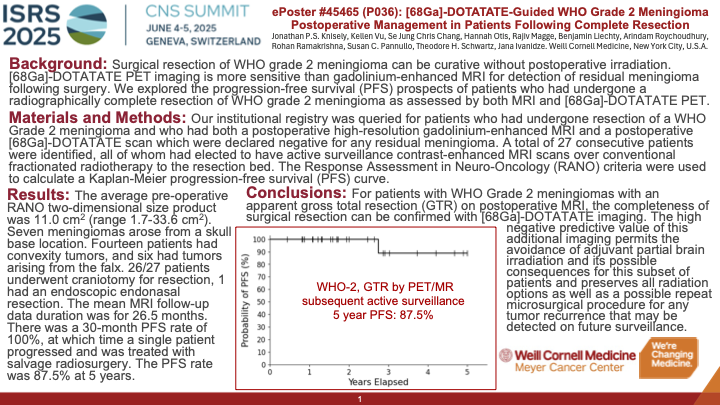
Materials & Methods: Our institutional registry was queried for patients who had undergone resection of a WHO Grade 2 meningioma and who had both postoperative high-resolution gadolinium-enhanced MRI and postoperative [68Ga]-DOTATATE scans which were declared negative for any residual meningioma. A total of 30 consecutive patients were identified, all of whom had elected to have active surveillance over conventional fractionated radiotherapy to the resection bed. Follow-up for all patients included contrast-enhanced MRI scans to monitor for any progression in the resection bed. The Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria were used to calculate a Kaplan-Meier progression-free survival (PFS) curve (Figure 1).
Results: The average pre-operative RANO two-dimensional size product was 11.5 cm2 (range 3.0-28.6 cm2). Half of the tumors arose from a skull base location (n=15; 50%). Nine patients had tumors located along the convexity (30%) and six had tumors arising from the falx (20%). All but 3 patients (10%) underwent craniotomy for resection, and those 3 individuals had endoscopic endonasal resections. The mean MRI follow-up data duration was for 23 months. There was a 30-month PFS rate of 100%, at which time a single patient progressed and was treated with salvage radiosurgery. The PFS rate was 83.3% at the time of maximum follow-up (5 years).
Conclusion: For patients with WHO Grade 2 meningiomas with an apparent gross total resection on postoperative MRI, the completeness of surgical resection can be confirmed with [68Ga]-DOTATATE imaging. The high negative predictive value of this additional imaging permits the avoidance of partial brain irradiation for this subset of patients and preserves all radiation options for any possible tumor recurrence that may be detected on surveillance.