Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is an effective treatment of trigeminal neuralgia (TN). Variations in dose delivery rate associated with total treatment time have been reported to affect the biological effectiveness of cobalt-based radiosurgery. In this study, we aimed to quantify the range of treatment delivery times in CyberKnife radiosurgery (CKRS) for TN and investigate its impact on the treatments’ bio-efficacy using the concept of biological effective dose (BED).
Treatment data of patients undergone CKRS for TN were retrospectively reviewed from the participating centers. Planning details were extracted from XML files stored in the CK database following treatment completion. For each case, time-resolved dose and dose-rate distributions were calculated per beam for every voxel comprising the target and brainstem using a ray tracing-based dose calculation algorithm developed in-house. BED distributions accounting for sublethal damage repair effects (BED_SRE) were obtained for both the target and brainstem along the lines described in Moutsatsos et al 2022 (Phys Med Biol 2022, 67, 135004). Studied variables included treatment delivery time, beam-on-time, target volume, prescription dose, maximum, minimum, average, and integral taget doses, as well as corresponding BED_SRE data.
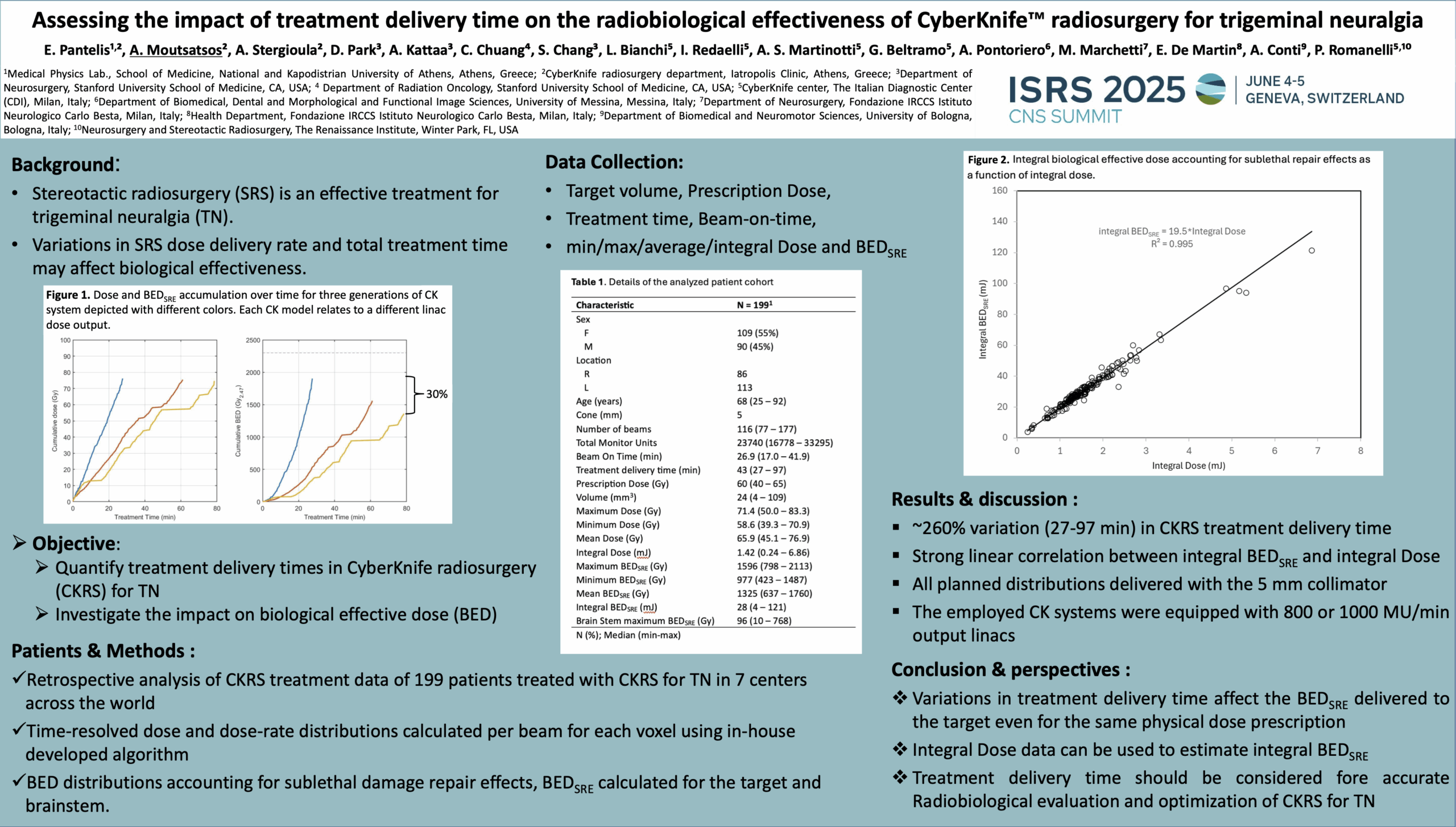
Planning data of 199 patients were evaluated and statistical analysis results are summarized in Table 1. The median age of patient cohort was 67 years, with a male to female ratio of 9/11. 56% of the patients had right and 44% left trigeminal neuralgia. Treatment was delivered using CK system models equipped with linear accelerators of nominal output rates of 800 and 1000 MU/min. A median dose of 60 Gy was prescribed at the periphery of the delineated nerve, having a median volume of 22 mm3. The median maximum and minimum dose values were 71.4 Gy and 59 Gy, respectively. All treatment plans used the 5 mm fixed cone. A median treatment delivery time of 43 min (range: 27 – 97 min) with median bean-on-time equal to 27 min (range: 17 – 42 min) was recorded. A strong linear correlation between integral BED_SRE and integral dose was found (Figure 1).
Treatment delivery time varied significantly among the different plans, ranging from 27 min to nearly 97 min for the same physical dose of 60 Gy. This variation correspondingly affected the BED_SRE delivered to the target. The Integral Dose data can be used to estimate the Integral BED_SRE using the proposed linear function.